In 3327, we like tackling different areas of web3. During one of our discussions, we decided to dive into the blockchain insurance market.
What exactly do we mean by blockchain insurance? We considered all the protocols/insurers that utilize the blockchain technology in their insurance product offer and operations.
That’s why we chose to conduct explorative research that will, as a result, help us all better understand how insurance protocols operate and what are the challenges present in decentralized insurance.
Before we go straight to the meat of the matter, here is a quick Insurance 101:
What is insurance?
Insurance has a long history; there are claims that it was created around 2000 BC in Babylon. Merchant receiving a loan paid the lender extra money in exchange for exemption of loan payment if the merchant’s shipment were stolen. However, We cannot present the importance of the insurance field without mentioning London’s Lloyd’s.
In the 17th century, a London coffeehouse was a meeting place for people seeking marine cargo protection and people willing to take those risks in exchange for a premium.
Workers would fill in a sheet of cargo and ship information, and the individuals who accepted that risk would sign with their names under its description. The coffee shop now is the world-famous Lloyds. Now, let’s do a quick Insurance terms overview:
- Underwriting is a risk assessment process to determine whether to accept or reject the risk.
- The point of insurance is to transfer and share risks.
- The individuals or companies that would like to transfer risk to other parties by paying a certain fee (premium) are called insured. The reason why the insured avoid the risk is that the loss is too volatile to bear.
- The party that accepts such risks and an associated fee (premium) is the insurer. Insurers are not averse to exposing themselves to the same risks as insured because of something called pooling and the law of large numbers. The essence of pooling risk is to spread losses of the few over the entire group. The law of large numbers states that the greater the number of exposures, the more closely will the actual results approach the expected average value.
What is the nature of Insurance and what are the benefits?
Insurance allows the insured to “trade” the risk of loss for the certainty of smaller payments. As a result, this ensures a stable cash flow since there are no extreme losses, and if they happen, they are covered by the insurance. As a result of this “stability” provided by insurance, there is less need for government assistance, saving public resources.
Insurance process in a centralized way:

- The application for insurance often starts with a quoting process where the amount to be paid in premiums is estimated according to the risk the client would like to manage. (1) After the application, the underwriting process occurs.
- The underwriter evaluates the information of the application and then accepts, and then “fine-tunes” the policy using the rating tables from the actuaries. Actuaries calculate premiums; in DeFi, this is done differently; more words on that in the later paragraphs. (2)
- After the underwriter accepts the application, the policy is issued. (3)
- If a loss occurs, the claims department examines the claim and asks the insured for the proof of loss before paying the insured amount. The payment depends on the amount of damage suffered and the decision of the claim department. (4)
When it comes to insurance with cryptocurrency with traditional insurers, we haven’t seen much movement there yet. But why is that the case? Here are the three main reasons in our opinion:
- Insurance is a heavily regulated field, which means that innovations are possible, but they are usually very slow.
- Cryptocurrency is still considered highly volatile by institutions.
- The adoption of cryptocurrency among the general public is still in the early stages.
That’s why we will be covering the growing DeFi Insurance market today.
DeFi Insurance refers to buying coverage against losses caused by events in decentralized finance. With various hacks and exploits over the years, the need for insuring users from the results of these events emerged. The DeFi Insurance field is big and continuously growing, with different protocols emerging. However, only 2% of all DeFi value was insured in 2021.
Primary protection offered is the capital protection against protocol hack/exploit risk, smart contract failures, or stablecoin crashes. The premium the user pays for a cover depends on the type of the cover, the insurance provider, and the cover duration. All the transactions are stored on the blockchain.
The “Decentralized” part of this type of insurance is that anybody can act as a coverage provider. They become providers by locking up capital in a capital pool of the insurance protocol, thus providing needed liquidity.
As coverage providers, they choose for which protocols or events they want to provide coverage. For example: If they are certain that a protocol is safe from exploits, they will prefer providing liquidity to the pool that covers that event.
Another big part of DeFi Insurance is verifying claims. The Insurance protocol’s community often does this. Considering the nature of insurance and pooling of risk, and collecting coverage from providers, they are often assembled as DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations).
This means that governance token holders participate in verifying claims. There are several ways of doing that, and we will be covering them in the following paragraphs.
Check this out!
How do some of these protocols operate?
The 3 competitors we will be covering in this blog post are:
- Nexus Mutual
- InsurAce.io
- Etherisc
Of course, more blockchain insurance protocols are present, but to keep this blog a somewhat short overview of DeFi Insurance, we will showcase three. For those willing to dig deeper, you can check our comprehensive research.
Nexus Mutual
Nexus Mutual is an Ethereum-based platform that offers insurance products led by community management and financials.
Membership in Nexus requires a one-off membership fee of 0.0020 ETH (~$5.50). However, users need to verify their identity following their Know Your Customer process to become a member. They also currently cannot accept members from 17 countries.
You can find all deployed contracts of Nexus Mutual here.
All information regarding cover, staking, and claims approvals/denies can be found here.
Nexus Mutual is set up as a DAO and offers three kinds of products:
- Protection against failures in any protocol used by users yield-bearing token (Ethereum only)
- Protection against failures in the individual protocol user has funds in, on any chain, but not in other protocols it uses.
- Protection against hacks and halted withdrawals on exchanges or custodial wallets
Nexus cover protects against loss of funds, not loss of value, except in the Yield Token Cover.
We will not cover products in great detail here, as they are pretty straightforward. More info on them can be found here.
Nexus does not provide cover where the covered tokens and the cover amount are not denominated in the same reference currency.
How does the cover become available for the end-user?
- When Risk Assessors stake NXM against a protocol, custodian or cover product, more cover is made available. The mutual places limits on the amount of cover to protect the mutual from being too exposed to any single risk. There are two limits, a Specific Risk Limit, and a Global Capacity Limit.
- Specific Risk limit means capacity on any particular risk is limited by the amount of staking on that risk. If there is no stake, the mutual cannot offer any cover. Specific Risk limit = capacity factor x net_staked_NXM.
- Global Capacity Limit is based on the financial resources of the Mutual and is there to ensure the mutual is not overly exposed to any particular risk, regardless of how much is staked. Global Capacity Limit = Minimum Capital Requirement In ETH (MCReth) x 20%
- As cover policies expire, the cover becomes available.
How are claims filed?
Claims are filed by submission. Members must provide cryptographic evidence of the loss (proof of loss), and Claim Assessors later assess their claim by voting. Assessors are financially incentivized to take a longer-term view as they are required to lock up a stake. This stake is then burned if there is evidence of fraudulent voting, addressed by the Advisory Board.
The Advisory board consists of five members of the founding team of Nexus Mutual and insurance industry experts. They are said to have:
- Technical Expertise in Smart Contract Security and blockchain
- Technical Expertise in Insurance and Mutuals
- General Expertise
The Advisory board is there to provide technical guidance to the members of the mutual and exercise the emergency functions if required.
This proposes a question: How do they keep the Advisory Board “in check” with Nexus’s decentralization principles?
Nexus does that by enabling members to kick-vote the Advisory Board members that they think are working maliciously. Board members can be replaced by another member if the membership base agrees. These proposals cannot be interfered with by the existing Advisory Board.
How are claims assessed at Nexus?
- All Covered members for a particular covered token will be assessed together for each claim event; and
- The face value of the covered token immediately prior to the claim event shall be set as part of the claims assessment process; and
- Following a successful claim vote, all Covered Members will be able to contribute their covered tokens and redeem their claim payment on a proportional basis up to the cover amount.
All protocols and custodial accounts can be covered by the platform, provided that risk assessors staked enough value against them. Risk Assessors (experienced auditors, capital providers) can stake value in the form of NXM tokens, thereby vouching for the security of the protocol/custodian and dropping the price of the cover.
NXM can be unstaked at any time, subject to a 30-day withdrawal period. When the cover is subsequently sold on a protocol or custodian, Risk Assessors earn proportional rewards in NXM equivalent to 50% of the cover premium. Suppose a claim is accepted and a payout occurs.
In that case, Risk Assessors staked against the protocol/custodian will have their staked NXM burnt on a proportional basis to facilitate the payout of the cover amount.
This may result in a Risk Assessors having some or all of their NXM staked against the protocol/custodian burnt to provide capital for the payout of the claim.
InsureAce.io
InsurAce.io is a multi-chain mutual insurance protocol created in April 2021. It offers products that cover 100+ protocols, 3 CEX, and 1 IDO platform.
Currently, they are deployed on Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, and Avalanche. InsurAce hasn’t yet adopted the DAO governance mechanism, although they are working on it.
You can find the current state of Insurace.io (Capital pool size, Active cover amount, Capital Ratios, etc.) here.
This protocol has four unique selling propositions :
- “0” Premium – The premiums are lower for their products. Their team designed portfolio-centric products to embrace risk diversification and developed models to optimize the cover cost. They did so by using advisors that are experts in the Insurance domain.
- Enriched Product Line – InsurAce.io also offers products that cover non-Ethereum DeFi protocols.
- Types of protocols and smart contract systems covered:
- Lending Protocols
- Decentralized Exchanges
- Derivative (e.g., Synthetix, Nexus Mutual)
- Asset (e.g. Badger, RenVM)
- Types of protocols and smart contract systems covered:
- SCR Mining – The participants earn $INSUR tokens by staking into the mining pool. The mutual capitals injected through staking will be managed with rigorous risk control models to dynamically adjust the Solvency Capital Requirement (SCR) and use the secured free capital for investment to control the mining speed accordingly.
- InsurAce tries to combat the low investment returns. Nexus mutual offers capital return to their providers from the premiums paid by users, which is low compared to the yield on Compound and Aave. This problem makes users prefer putting their funds elsewhere instead of the Insurance Protocol. InsurAce combats this by offering users:
- Option to invest directly in the investment product depending on their risk aversion
- Option to stake in the mutual pool and get the investment carries and $INSUR tokens as rewards
InsurAce operates similarly to the traditional insurance companies using the insurance and investment arms.
The insurance arm maintains reserve pools which maintain the solvency for claim coverage based on risk exposure. The investment arm maintains investment pools that generate carry to subsidize claims and attract investors with risk appetite.
The free capital in the insurance capital pool can be placed into the investment pool to gain a higher yield, while the insurance arm will protect the investment activities. Meanwhile, the investment arm’s yield will complement the premium on the insurance side and reduce the cover cost for customers.
Pricing model
InsurAce adopts the new actuary-based pricing model in order to assess the expected loss of insurance products fairly, reduce costs and enhance capability.
The model’s main inputs are the number/amount of claims and number/amount of exposures in a given time period, which will be used for selecting and training two separate models – the frequency model and the severity model.
Frequency modeling produces a model that calibrates the probability of a given number of losses occurring during a specific period, while severity modeling produces the distribution of loss amounts and sets the level of deductible and limit of the coverage amount.
These models are then combined to solve aggregate loss. After that, the decided aggregate loss is incorporated into the risk factors of protocols, and the premiums are then calculated. The model’s parameters rely on historical data to devise and validate. They plan on taking this further with new Machine Learning methodologies.
How is Risk Assessment of new protocols taken care of?
InsurAce’s Advisory Board performs a preliminary risk assessment on the new protocols first. InsurAce will also work with auditing firms if extra complexity or challenges exist. After that Advisory Board provides a report and rates the protocol 1 to 5.
After they rate it, the protocol will go through the community risk assessment. Members who participate in the process get INSUR tokens as an incentive.
How are claims assessed by InsurAce.io?
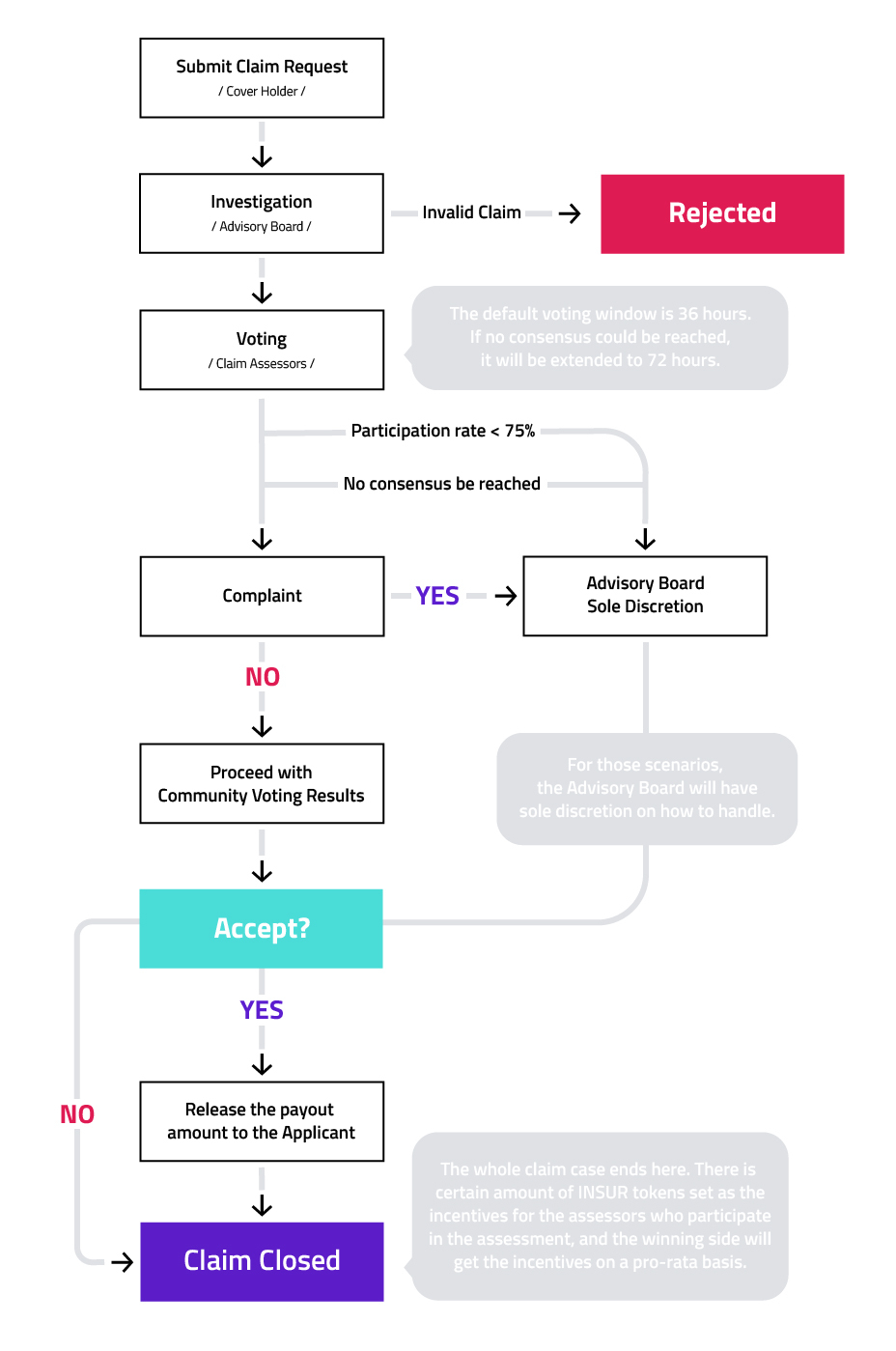
This diagram shows us the InsureAce’s claims Assessment process in an intuitive way.
$INSUR token holders can stake the $INSUR tokens to become the community Claim Assessors. The Claim Assessor will be entitled to the right to vote in each claim assessment and earn $INSUR tokens as a reward if their votes match with the voting result.
During each voting session, the more tokens the user stake, the more voting tickets they will get (*capped at 5% of the total votes), and the more rewards they will receive.
Etherisc
Etherisc tries to tackle insurance a little differently, and they do that by tackling “real world” risk events.
Etherisc is a protocol to collectively build insurance products. Common infrastructure, product templates, and insurance license-as-a-service make a platform that allows anyone to create their own insurance products. The first product Etherisc offered was FlightDelay Insurance.
Products currently licensed are:
- Crop Insurance
- FlightDelay Insurance
Products currently in design are:
- Hurricane Protection
- Crypto Wallet Insurance
- Collateral Protection for Crypto backed Loans
- Social Insurance (death, serious illness).
Users can also build their own insurance products.
How does the Etheriscs economy work?
DIP(Etheriscs token) tokens act as the native internal currency that is inseparable from the protocol and network of its users. DIP tokens are needed to earn transaction fees (% of insurance premiums or fixed cost), incentivize and reward platform users to bring risk to the network, build and maintain risk transfer products.
The total supply of Etherisc tokens is 1 Billion.
DIP tokens give users access to the Decentralized Insurance Platform. Participants provide collateral (bond) to guarantee future performance, availability, and service levels by staking the DIP token. Staking also signals quality and reputation.
As a result, participants can earn money monetizing their skills, software (for example, risk models or UI/UX), risk capital, insurance licenses, claim processing, or regulatory compliance/reporting services.
Who are the participants in the protocol, and how do they use the DIP token?
- Customers – Universal currency to buy insurance products.
- Risk model Providers and Actuaries – Staking/Reward for providing or updating risk models.
- Data providers and oracles – Reward for giving data. The reward for providing access to data pools. Staking / Reward for providing reliable oracles.
- Sales Agents – Reward for distribution of products.
- Claim Agents – Reward for the provided service.
- License providers – Staking tokens to provide capital for a license provider, paying fees for licenses.
- Product managers – Reward for service
As we can see above, some of the Etherisc protocol participants are also participants in the traditional insurance organizations.
FlightDelay Insurance example
Etherisc launched its “FlightDelay” insurance product on January 20th, 2022, by utilizing Chainlink data to check if a flight has been canceled or delayed. The product is now available for passenger flights globally, and policies can be purchased via Etheriscs FlightDelay Portal. All policy payments are processed through the Gnosis Chain.
Etherisc uses smart contracts and Chainlink data to issue insurance policies. This product provides policyholders with a transparent and secure end-to-end solution for flight insurance.
All of this couldn’t be possible without Chainlink oracles which provide reliable; real-time data feeds to ensure accurate flight information is used when assessing insurance claims. Oracle failure risk is mitigated with the use of Chainlink’s multiple decentralized data oracles.
What are some of the challenges of blockchain insurance?
- In creating these kinds of products, there needs to be significant effort both in developing and initial investment. Protocols utilize Advisory Boards of insurance experts to create their products.
- State regulation is a big factor in insurance to protect the policyholders from malicious insurance offerers. This can be a problem when insuring, depending on the states’ attitude towards cryptocurrency.
- Handling claims is often left to the community, incentivizing just behavior by staking.
- Collecting adequate capital, in the beginning is also one of the significant problems.
- Protocols with less staked pools have higher premiums in most cases, showing us that risk assessment is usually hard to do with new protocols.
- There is a limited cover capacity.
- Usually, there is no cross-chain coverage which limits the protection capability of DeFi protocols on other chains.
- Lack of protection diversity: most products offered are limited compared to the broad coverage of risk types in the traditional insurance market.
- Insuring “real-world” events risk is almost non-existent. Etherisc offers two products that utilize Oracles (they are working on more products currently), but our assumption is that there is still no market need for these kinds of products; thus, there is not much movement in this direction. However, utilizing Oracles in traditional products is interesting, and we think it should be looked into more.
For more research like this, make sure to visit the 3327 research database.



